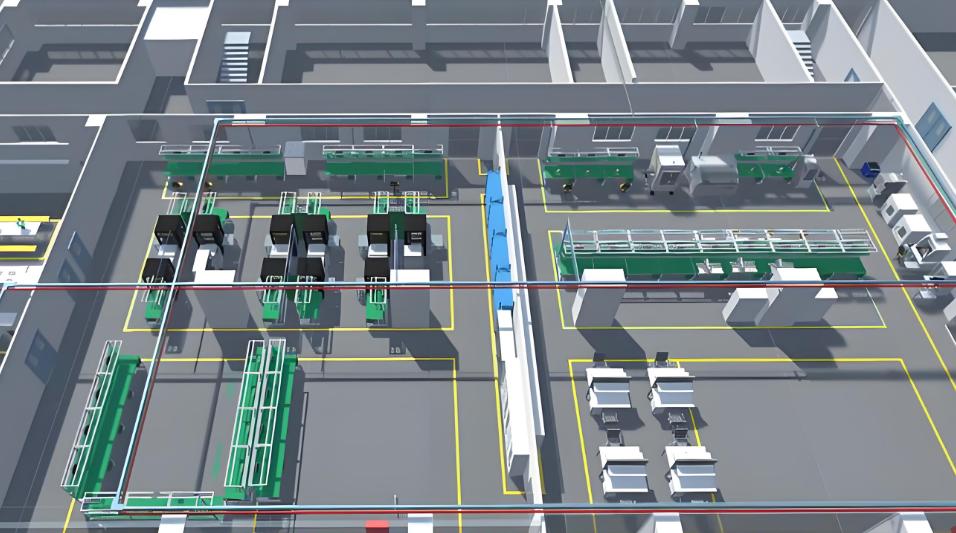
Factory layouts design involves designing and planning the physical arrangement of equipment, workstations, storage, and personnel in a manufacturing facility to optimize workflow, efficiency, and safety. A well-designed factory layout can significantly improve the efficiency, productivity, and safety of manufacturing operations. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the services you can provide:
Here are the services you can request through this platform with factory layout design:
1. Factory Layout Design and Planning:
Initial Layout Consultation: Offer expert consultation to analyze a factory's operational needs, objectives, and constraints. Understand the process flows and develop an initial factory layout plan.
Examples: Layout for new factories, plant expansions, or renovations.
Space Optimization: Help clients optimize available space by determining the best layout for equipment, machinery, storage, and workflow. This involves ensuring efficient use of floor space to improve throughput while minimizing material handling.
Examples: Maximizing space usage in a warehouse or production facility.
Production Line Layout: Design production line layouts that organize machinery and workstations in a way that minimizes waste, bottlenecks, and unnecessary movements.
Examples: Assembly lines, continuous flow processes, or batch production lines.
Flexible Layout Planning: Provide flexible factory layouts that allow for future modifications or scalability as the business grows or shifts its product lines.
Examples: A layout that supports various manufacturing methods such as assembly, machining, or packaging.
2. Flow Analysis and Optimization:
Material Flow Optimization: Design layouts that optimize the movement of raw materials, components, and finished goods throughout the factory. Reduce unnecessary transportation distances to improve material flow and minimize lead times.
Examples: Streamlining material flow between warehouses, production areas, and shipping docks.
Employee Workflow Design: Plan the layout to ensure efficient movement of personnel and minimize worker fatigue by creating ergonomic workstations and ensuring proper access to tools, materials, and equipment.
Examples: Designing workstations for maximum worker productivity in an assembly line.
Process Flow Design: Organize the layout so that the sequence of operations is logically structured, reducing interruptions and improving production speed.
Examples: Machine shops, food processing plants, or automotive assembly lines.
Inventory and Storage Optimization: Plan and design storage areas (e.g., raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods) to improve inventory management and minimize storage costs.
Examples: Racking systems, shelving designs, and inventory control systems.
3. Ergonomics and Workplace Design:
Ergonomic Workstations: Design ergonomic workstations that improve worker comfort, reduce repetitive strain injuries, and increase productivity by tailoring workstations to specific tasks and employee needs.
Examples: Adjustable-height tables, specialized tools for assembly tasks, and anti-fatigue flooring.
Employee Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the layout complies with safety regulations (e.g., OSHA, local health and safety standards) by incorporating safety features like emergency exits, fire exits, clear walkways, and proper lighting.
Examples: Safety signage, proper placement of emergency equipment (fire extinguishers, eyewash stations), and proper aisle widths.
Cleanroom and Specialized Areas: Provide design for cleanrooms or specialized areas that need to meet specific hygiene, cleanliness, or environmental standards.
Examples: Pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing plants, or semiconductor fabrication facilities.
4. 3D Factory Layout Design and Simulation:
3D Factory Layout Visualization: Offer 3D visualization of factory layouts using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This allows clients to visualize the factory's workflow and identify any inefficiencies or potential improvements before physical implementation.
Examples: Virtual walkthroughs of factory layouts to assess workflow, space usage, and material handling.
Simulation of Operations: Simulate the performance of various factory layouts in terms of productivity, material flow, and worker movement using simulation software to predict how the design will operate under real conditions.
Examples: Simulation of production line operations to test for potential bottlenecks or delays.
5. Lean Manufacturing and Waste Reduction:
Lean Layout Design: Implement lean principles to design factory layouts that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and streamline production processes. This includes applying techniques like 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Kanban, or value stream mapping to reduce inefficiencies.
Examples: Eliminating excess inventory, optimizing equipment placement, or reducing waiting times between processes.
Cellular Manufacturing Design: Organize the factory layout using cellular manufacturing concepts, where machines are arranged in groups (cells) to produce a specific product or product family with minimal handling.
Examples: Automotive component manufacturing or custom product assembly.
Kanban and Pull Systems: Incorporate Kanban systems into factory layouts to improve inventory management and reduce overproduction by using visual signals to control the flow of materials.
Examples: Automated or semi-automated factories that rely on lean principles.
6. Material Handling Systems Design:
Automated Material Handling Systems (AMHS): Design layouts with integrated automated material handling systems (e.g., conveyors, robotic arms, automated guided vehicles) to efficiently transport materials between workstations.
Examples: Assembly lines for electronics, packaging lines, or automotive manufacturing.
Manual and Semi-Automated Handling Systems: Design manual or semi-automated material handling systems such as forklifts, pallet racks, or carts for efficient material movement in smaller-scale operations or warehouses.
Examples: Small-scale manufacturing operations, warehouses, or distribution centers.
7. Facility Services Planning:
Utilities and Infrastructure Design: Plan the layout of essential utilities and infrastructure, including power supply, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), water supply, and compressed air systems.
Examples: Optimizing the placement of ventilation systems in manufacturing plants or designing water treatment systems for food production.
Waste Disposal Systems: Plan and design the waste management and disposal systems within the factory to minimize environmental impact, such as sorting stations, recycling areas, or hazardous waste zones.
Examples: Medical waste disposal in healthcare facilities, or waste reduction systems in manufacturing plants.
8. Building Design and Integration:
Factory Building Design: Provide architectural planning for the construction or renovation of factory buildings, ensuring the layout supports operational needs. This includes floor plan design, structural planning, and ensuring that the building adheres to local building codes and regulations.
Examples: Designing new factory buildings, warehouses, or distribution centers.
Mezzanine and Vertical Space Planning: Design the use of vertical space (e.g., mezzanines, multi-level storage) to maximize space efficiency in existing buildings or for new facilities.
Examples: Storing goods or materials on a mezzanine to free up floor space for production.
9. Energy and Sustainability Planning:
Sustainable Factory Layout: Design factory layouts with energy efficiency and sustainability in mind, including renewable energy sources, optimized lighting systems, and minimizing energy consumption in production areas.
Examples: Incorporating solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and natural lighting in factory designs.
Green Manufacturing Practices: Integrate green manufacturing principles in the layout to minimize environmental impact, such as efficient water use, waste reduction, and the recycling of materials.
Examples: Wastewater recycling systems, low-energy machinery, or sustainable material sourcing.
10. Change Management and Layout Implementation:
Factory Layout Implementation Support: Provide implementation support by overseeing the physical installation of the factory layout, including the placement of machinery, workstations, and storage areas.
Examples: Guiding the installation of new equipment, ensuring that the layout is followed during construction or renovation.
Relocation and Expansion: Help clients plan for factory relocation or expansion, ensuring minimal disruption to production and smooth transitions to new layouts.
Examples: Relocating production lines or setting up new facilities to meet demand growth.
Factory layouts design involves designing and planning the physical arrangement of equipment, workstations, storage, and personnel in a manufacturing facility to optimize workflow, efficiency, and safety. A well-designed factory layout can significantly improve the efficiency, productivity, and safety of manufacturing operations. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the services you can provide:
Here are the services you can request through this platform with factory layout design:
1. Factory Layout Design and Planning:
Initial Layout Consultation: Offer expert consultation to analyze a factory's operational needs, objectives, and constraints. Understand the process flows and develop an initial factory layout plan.
Examples: Layout for new factories, plant expansions, or renovations.
Space Optimization: Help clients optimize available space by determining the best layout for equipment, machinery, storage, and workflow. This involves ensuring efficient use of floor space to improve throughput while minimizing material handling.
Examples: Maximizing space usage in a warehouse or production facility.
Production Line Layout: Design production line layouts that organize machinery and workstations in a way that minimizes waste, bottlenecks, and unnecessary movements.
Examples: Assembly lines, continuous flow processes, or batch production lines.
Flexible Layout Planning: Provide flexible factory layouts that allow for future modifications or scalability as the business grows or shifts its product lines.
Examples: A layout that supports various manufacturing methods such as assembly, machining, or packaging.
2. Flow Analysis and Optimization:
Material Flow Optimization: Design layouts that optimize the movement of raw materials, components, and finished goods throughout the factory. Reduce unnecessary transportation distances to improve material flow and minimize lead times.
Examples: Streamlining material flow between warehouses, production areas, and shipping docks.
Employee Workflow Design: Plan the layout to ensure efficient movement of personnel and minimize worker fatigue by creating ergonomic workstations and ensuring proper access to tools, materials, and equipment.
Examples: Designing workstations for maximum worker productivity in an assembly line.
Process Flow Design: Organize the layout so that the sequence of operations is logically structured, reducing interruptions and improving production speed.
Examples: Machine shops, food processing plants, or automotive assembly lines.
Inventory and Storage Optimization: Plan and design storage areas (e.g., raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods) to improve inventory management and minimize storage costs.
Examples: Racking systems, shelving designs, and inventory control systems.
3. Ergonomics and Workplace Design:
Ergonomic Workstations: Design ergonomic workstations that improve worker comfort, reduce repetitive strain injuries, and increase productivity by tailoring workstations to specific tasks and employee needs.
Examples: Adjustable-height tables, specialized tools for assembly tasks, and anti-fatigue flooring.
Employee Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the layout complies with safety regulations (e.g., OSHA, local health and safety standards) by incorporating safety features like emergency exits, fire exits, clear walkways, and proper lighting.
Examples: Safety signage, proper placement of emergency equipment (fire extinguishers, eyewash stations), and proper aisle widths.
Cleanroom and Specialized Areas: Provide design for cleanrooms or specialized areas that need to meet specific hygiene, cleanliness, or environmental standards.
Examples: Pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing plants, or semiconductor fabrication facilities.
4. 3D Factory Layout Design and Simulation:
3D Factory Layout Visualization: Offer 3D visualization of factory layouts using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This allows clients to visualize the factory's workflow and identify any inefficiencies or potential improvements before physical implementation.
Examples: Virtual walkthroughs of factory layouts to assess workflow, space usage, and material handling.
Simulation of Operations: Simulate the performance of various factory layouts in terms of productivity, material flow, and worker movement using simulation software to predict how the design will operate under real conditions.
Examples: Simulation of production line operations to test for potential bottlenecks or delays.
5. Lean Manufacturing and Waste Reduction:
Lean Layout Design: Implement lean principles to design factory layouts that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and streamline production processes. This includes applying techniques like 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Kanban, or value stream mapping to reduce inefficiencies.
Examples: Eliminating excess inventory, optimizing equipment placement, or reducing waiting times between processes.
Cellular Manufacturing Design: Organize the factory layout using cellular manufacturing concepts, where machines are arranged in groups (cells) to produce a specific product or product family with minimal handling.
Examples: Automotive component manufacturing or custom product assembly.
Kanban and Pull Systems: Incorporate Kanban systems into factory layouts to improve inventory management and reduce overproduction by using visual signals to control the flow of materials.
Examples: Automated or semi-automated factories that rely on lean principles.
6. Material Handling Systems Design:
Automated Material Handling Systems (AMHS): Design layouts with integrated automated material handling systems (e.g., conveyors, robotic arms, automated guided vehicles) to efficiently transport materials between workstations.
Examples: Assembly lines for electronics, packaging lines, or automotive manufacturing.
Manual and Semi-Automated Handling Systems: Design manual or semi-automated material handling systems such as forklifts, pallet racks, or carts for efficient material movement in smaller-scale operations or warehouses.
Examples: Small-scale manufacturing operations, warehouses, or distribution centers.
7. Facility Services Planning:
Utilities and Infrastructure Design: Plan the layout of essential utilities and infrastructure, including power supply, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), water supply, and compressed air systems.
Examples: Optimizing the placement of ventilation systems in manufacturing plants or designing water treatment systems for food production.
Waste Disposal Systems: Plan and design the waste management and disposal systems within the factory to minimize environmental impact, such as sorting stations, recycling areas, or hazardous waste zones.
Examples: Medical waste disposal in healthcare facilities, or waste reduction systems in manufacturing plants.
8. Building Design and Integration:
Factory Building Design: Provide architectural planning for the construction or renovation of factory buildings, ensuring the layout supports operational needs. This includes floor plan design, structural planning, and ensuring that the building adheres to local building codes and regulations.
Examples: Designing new factory buildings, warehouses, or distribution centers.
Mezzanine and Vertical Space Planning: Design the use of vertical space (e.g., mezzanines, multi-level storage) to maximize space efficiency in existing buildings or for new facilities.
Examples: Storing goods or materials on a mezzanine to free up floor space for production.
9. Energy and Sustainability Planning:
Sustainable Factory Layout: Design factory layouts with energy efficiency and sustainability in mind, including renewable energy sources, optimized lighting systems, and minimizing energy consumption in production areas.
Examples: Incorporating solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and natural lighting in factory designs.
Green Manufacturing Practices: Integrate green manufacturing principles in the layout to minimize environmental impact, such as efficient water use, waste reduction, and the recycling of materials.
Examples: Wastewater recycling systems, low-energy machinery, or sustainable material sourcing.
10. Change Management and Layout Implementation:
Factory Layout Implementation Support: Provide implementation support by overseeing the physical installation of the factory layout, including the placement of machinery, workstations, and storage areas.
Examples: Guiding the installation of new equipment, ensuring that the layout is followed during construction or renovation.
Relocation and Expansion: Help clients plan for factory relocation or expansion, ensuring minimal disruption to production and smooth transitions to new layouts.
Examples: Relocating production lines or setting up new facilities to meet demand growth.
[ Retract  ]
]